A Loopback4 LLM Chat Extension¶
Overview¶
A Loopack4 based component to integrate a basic Langgraph.js based endpoint in your application which can use any tool that you register using the provided decorator.
Installation¶
Install AIIntegrationsComponent using npm;
Basic Usage¶
Configure and load the AIIntegrations component in the application constructor as shown below.
LLM Providers¶
Ollama¶
To need the Ollama based models, install the package - @langchain/ollama and update your application.ts -
Gemini¶
To use the Gemini based models, install the package - @google/generative-ai and @langchain/google-genai and update your application.ts -
Cerebras¶
To use the Cerebras based models, install the package - @langchain/cerebras and update your application.ts -
Anthropic¶
To use the Anthropic based models, install the package - @langchain/anthropic and update your application.ts -
OpenAI¶
To use the OpenAI models, install the package - @langchain/openai and update your application.ts -
Bedrock¶
To use the Bedrock based models, install the package - @langchain/aws and update your application.ts -
This binding would add an endpoint /generate in your service, that can answer user's query using the registered tools. By default, the module gives one set of tools through the DbQueryComponent
Limiters¶
The package provides a way to limit the usage of the LLM Chat functionality by binding a provider on the key AiIntegrationBindings.LimitStrategy that follows the interface - ILimitStrategy.
The packages comes with 3 strategies by default that are bound automatically on the basis of AiIntegrationBindings.Config -
- ChatCountStrategy - Applies limits per user based on number of chats. It is used if only
chatLimitandperiodis provided intokenCounterConfig. - TokenCountStrategy - Applies a fixed limit per user based on number of tokens used. It is used if
tokenLimitandperiodare provided withbufferTokenas optional field that determines that how much buffer to keep while checking for token limit. - TokenCountPerUserStrategy - Applies token based limit similar to
TokenCountStrategyexcept the number of tokens commes from user permissionTokenUsage:NUMBERin the user's token. It applies if onlyperiodis set intokenCounterConfig, it also works withbufferTokenjust likeTokenCountStrategy.
DbQueryComponent¶
This component provides a set of pre-built tools that can be plugged into any Loopback4 application -
- generate-query - this tool can be used by the LLM to generate a database query based on user's prompt. It will return a
DataSetinstead of the query directly to the LLM. - improve-query - this tool takes a
DataSet's id and feedback from the user, and uses it to modify the existingDataSetquery. Users can also vote on datasets via the dataset actions endpoint. - ask-about-dataset - this tool takes a
DataSet's id and a user prompt, and tries to answer user's question about the database query. Note that it can not run the query.
Database Schema¶
The component uses a dedicated chatbot schema with the following tables:
- datasets - Stores generated SQL queries with metadata including description, prompt, tables involved, and schema hash
- dataset_actions - Tracks user actions on datasets (votes, comments, improvements)
- chats - Stores chat sessions with metadata and token usage
- messages - Stores individual messages within chats
Dataset Feedback System¶
Users can provide feedback on generated datasets through the dataset actions endpoint. Each dataset can receive votes and comments, which can be used to improve future query generation. The system tracks:
- Vote count for each dataset
- User comments and suggestions
- Improvement history
- Creation and modification timestamps
Query Generation Flow¶
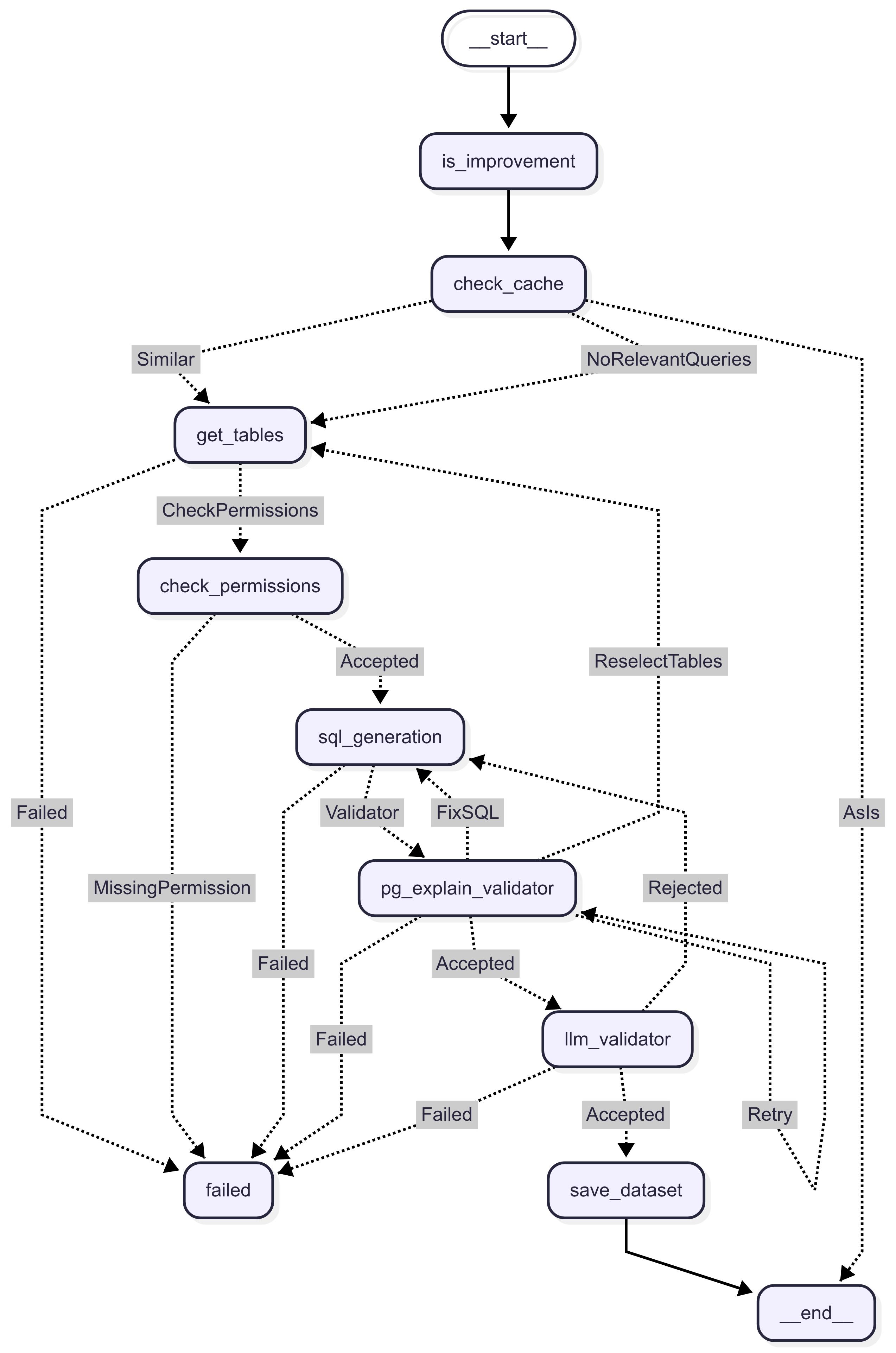
VisualizerComponent¶
The VisualizerComponent extends the LLM Chat functionality by providing intelligent data visualization capabilities. This component automatically generates charts and graphs based on database query results, making data insights more accessible and visually appealing.
Features¶
- Automatic Visualization Selection - The system intelligently selects the most appropriate visualization type based on the data structure and user prompt
- Multiple Chart Types - Supports bar charts, line charts, and pie charts out of the box
- LLM-Powered Configuration - Uses AI to generate optimal chart configurations including axis selection, orientation, and styling
- Seamless Integration - Works directly with datasets generated by the DbQueryComponent
Available Visualizers¶
The component includes three built-in visualizers:
Bar Chart Visualizer (src/components/visualization/visualizers/bar.visualizer.ts:13)¶
- Best for: Comparing values across different categories or showing trends over time
- Configuration: Automatically determines category column (x-axis) and value column (y-axis)
- Options: Supports both vertical and horizontal orientations
Line Chart Visualizer (src/components/visualization/visualizers/line.visualizer.ts)¶
- Best for: Displaying trends and changes over time
- Configuration: Optimized for time-series data and continuous variables
Pie Chart Visualizer (src/components/visualization/visualizers/pie.visualizer.ts)¶
- Best for: Showing proportions and percentages of a whole
- Configuration: Automatically identifies categorical data and corresponding values
Usage¶
Basic Setup¶
Generate Visualization Tool¶
The component provides a generate-visualization tool that can be used by the LLM to create visualizations:
- Input: Takes a user prompt and dataset ID from a previously generated query
- Process: Automatically selects the best visualization type and generates optimal configuration
- Output: Renders the visualization in the UI for the user
Example Usage Flow¶
- User asks: "Show me sales by region as a chart"
- LLM uses
generate-querytool to create a dataset with sales data by region - LLM uses
generate-visualizationtool with the dataset ID - System selects bar chart as the most appropriate visualization
- Chart is rendered with regions on x-axis and sales values on y-axis
Visualization Graph Flow¶
The visualization process follows a structured graph workflow (src/components/visualization/visualization.graph.ts:9):
- Get Dataset Data - Retrieves the dataset and query information
- Select Visualization - Chooses the most appropriate chart type based on data structure
- Render Visualization - Generates the final chart configuration and displays it
Creating Custom Visualizers¶
You can extend the system with custom visualizers by implementing the IVisualizer interface (src/components/visualization/types.ts:4):
Configuration¶
The visualizer component automatically registers all available visualizers and makes them available to the LLM. No additional configuration is required for basic usage. You can register a new visualizer using the @visualizer decorator on a class following the IVisualizer interface.
Integration with DbQueryComponent¶
The visualizer component works seamlessly with the DbQueryComponent:
- Use database query tools to generate datasets
- The visualization tool automatically accesses dataset metadata including:
- SQL query structure
- Query description
- User's original prompt
- This context helps generate more accurate and relevant visualizations
Providing Context¶
There are two ways to provide context to the LLM -
Global Context¶
Global context can be provided as an array of strings through a binding on key DbQueryAIExtensionBindings.GlobalContext. This binding can be a constant or come through a dynamic provider, something like this -
in application.ts -
Model Context¶
Each model can have associated context in 3 ways -
- Model description - this is the primary description of the model, it is used to select model for generation, so it should only define the purpose of the model itself.
- Model context - this is secondary information about the model, usually defining some specific details about the model that must be kept in mind while using it. NOTE - These values should always include the model name. This must be information that is applicable to overall model usage, or atleast to multiple columns, and not related to any single field of the model.
- Property description - this is the description for a property of a model, providing context for the LLM on how to use and understand a particular property.
Usage¶
You just need to register your models in the configuration of the component, and if the Models have proper and detailed descriptions, the tools should be able to answer the user's prompts based on those descriptions.
Connectors¶
The package comes with 3 connectors by default -
- PgConnector - basic connector for PostgreSQL databases
- SqlLiteConnector - basic connector SqlLite databases, can be used for testing
- PgWithRlsConnector - Connector for PostgreSQL databases with support for Row Security Policies. Refer
PgWithRlsConnectorfor more details.
You can write your own connector by following the IDbConnector interface and and binding it on DbQueryAIExtensionBindings.Connector.
By default, the package binds PgWithRlsConnector but if you are not planning to use row security policies or default conditions, you can bind PgConnector -
Default Conditions¶
The package allows binding an optional provider on key DbQueryAIExtensionBindings.DefaultConditions that are applied on every query generated by the LLM. NOTE This only works for connectors that support this option.
As of now, the only provider that supports this is PgWithRlsConnector.
PgWithRlsConnector¶
You can take advantage of the DbQueryAIExtensionBindings.DefaultConditions by using this connector with a PostgreSQL database. To use this you need to first setup your database to use Row Security Policies. You can use an SQL script that looks something like this to do this -
Once the policies are setup, you can bind the provider for DbQueryAIExtensionBindings.DefaultConditions -
Writing Your Own Tool¶
You can register your own tools by simply using the @graphTool() decorator and implementing the IGraphTool interface. Any such class would be automatically registered with the /generate endpoint and the LLM would be able to use it as a tool.
Observability¶
With Langsmith¶
You can enable langsmith observability by simply adding the Langsmith env variables. Refer this for more details.
With Langfuse¶
You can enable Langfuse based tracing with the following steps -
- install the following packages -
- adding the following component in your LB4 application -
- set up langfuseSpanProcessor -
- setup env -
Testing¶
Generation Acceptance Builder¶
The generation.acceptance.builder.ts file provides a utility to run acceptance tests for the llm-chat-component. These tests validate the functionality of the /reply endpoint and ensure that the generated SQL queries and their results align with expectations.
Overview¶
This builder facilitates the execution of multiple test cases, each defined with specific prompts, expected results, and configurations. It also generates detailed reports to analyze the performance and correctness of the tests.
Key Features¶
- Dynamic Prompt Parsing: Replaces placeholders in prompts with environment-specific values.
- Token Generation: Creates JWT tokens with required permissions for test execution.
- Query Execution: Executes the generated SQL queries and compares the results with expected outputs.
- Detailed Reporting: Generates markdown reports with metrics such as success rates, token usage, and execution times.
Usage¶
Importing the Builder¶
Running Tests¶
To use the builder, define your test cases as an array of GenerationAcceptanceTestCase objects and pass them to the generationAcceptanceBuilder function along with the required parameters.
Example¶
Parameters¶
cases: An array of test cases to execute.client: The LoopBack test client.app: The LoopBack application instance.countPerPrompt: Number of iterations per test case (default: 1).writeReport: Whether to generate a markdown report (default: false).
Test Case Structure¶
Each test case should follow the GenerationAcceptanceTestCase interface:
Report Generation¶
The builder generates a markdown report summarizing the test results. The report includes:
- Success metrics
- Time metrics
- Token usage metrics
- Detailed results for each test case
- Failed queries with actual and expected results
The report is saved in the llm-reports directory with a filename based on the model name.
Environment Variables¶
The builder relies on the following environment variables:
SAMPLE_DEAL_NAME: Default value for<testDeal>placeholder.TEST_TENANT_ID: Tenant ID for token generation.JWT_SECRET: Secret key for signing JWT tokens.JWT_ISSUER: Issuer for JWT tokens.
Dependencies¶
@loopback/testlab@loopback/core@loopback/repository@sourceloop/corejsonwebtokencryptofs






